
Back Тэсты выяўлення антыгена малярыі Byelorussian ম্যালেরিয়া অ্যান্টিজেন সনাক্তকরণ পরীক্ষা Bengali/Bangla Δοκιμές ανίχνευσης αντιγόνου ελονοσίας Greek Pruebas de detección de antígenos de la malaria Spanish Malaaria antigeeni tuvastamise testid Estonian Malarian antigeenin havaitsemistestit Finnish Tests de détection de l'antigène du paludisme French Probas de detección de antíxenos da malaria Galician मलेरिया एंटीजन डिटेक्शन टेस्ट Hindi Maláriaantigén kimutatására szolgáló tesztek Hungarian
| Malaria antigen detection tests | |
|---|---|
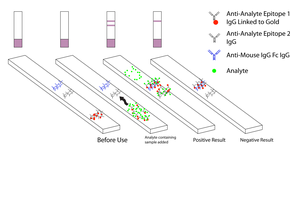 A schematic diagram of a dipstick | |
| Purpose | diagnosis of malaria... |
Malaria antigen detection tests are a group of commercially available rapid diagnostic tests of the rapid antigen test type that allow quick diagnosis of malaria by people who are not otherwise skilled in traditional laboratory techniques for diagnosing malaria or in situations where such equipment is not available. There are currently over 20 such tests commercially available (WHO product testing 2008). The first malaria antigen suitable as target for such a test was a soluble glycolytic enzyme Glutamate dehydrogenase.[1][2][3] None of the rapid tests are currently as sensitive as a thick blood film, nor as cheap. A major drawback in the use of all current dipstick methods is that the result is essentially qualitative. In many endemic areas of tropical Africa, however, the quantitative assessment of parasitaemia is important, as a large percentage of the population will test positive in any qualitative assay.
- ^ Ling IT.; Cooksley S.; Bates PA.; Hempelmann E.; Wilson RJM. (1986). "Antibodies to the glutamate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum" (PDF). Parasitology. 92 (2): 313–324. doi:10.1017/S0031182000064088. PMID 3086819. S2CID 16953840.
- ^ Rodríguez-Acosta A, Domínguez NG, Aguilar I, Girón ME (1998). "Characterization of Plasmodium falciparum glutamate dehydrogenase-soluble antigen". Braz J Med Biol Res. 31 (9): 1149–1155. doi:10.1590/S0100-879X1998000900008. PMID 9876282.
- ^ Li Y, Ning YS, Li L, Peng DD, Dong WQ, Li M (2005). "Preparation of a monoclonal antibodies against Plasmodium falciparum glutamate dehydrogenase and establishment of colloidal gold-immunochromatographic assay". Di Yi Jun Yi da Xue Xue Bao = Academic Journal of the First Medical College of PLA. 25 (4): 435–438. PMID 15837649.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search